Living with the planet

Targets and progress
In 2024, we set several targets related to “Living with the planet,” one of the materiality topics in the JT Group Sustainability Targets. Following up on efforts to achieve the objectives of the JT Group Environment Plan 2030, they have been updated to more ambitious targets, with some new targets added as well.
Targets |
Representative targets |
|---|---|
Biodiversity impact assessment |
Each JT Group business will perform an assessment to evaluate its impact and dependence on ecosystems, including biodiversity aspects. We will complete impact assessments for our tobacco business in 2024, and for our pharmaceutical and processed food businesses by 2025. |
Emissions reduction |
All JT Group operations will be carbon neutral by 2030, and the entire value chain will achieve Net-Zero by 2050.
|
Renewable energy |
Convert all sources of energy used throughout the JT Group to renewable in order to achieve Net-Zero GHG emissions by 2050.
|
Protecting water |
|
Enhancing biodiversity - No deforestation, no conversion |
|
Waste reduction |
|
Designing for circularity - Packaging, product and device |
|
Sustainable agriculture |
Our tobacco business will eliminate the use of Criterion 1 Highly Hazardous Pesticides (HHPs) from its tobacco leaf supply chain in 2024 and all HHPs by 2040. 100% of our directly contracted growers will adopt the Good Agricultural Practices (GAP) Protocol of our tobacco business by 2030. |
Road map to Net-Zero
The JT Group is working to make its operations carbon neutral by 2030 and achieve Net-Zero GHG emissions across the entire value chain by 2050, and its 2030 reduction targets have been validated by SBTi. In June 2024, we submitted a commitment letter declaring to make science-based GHG emissions reduction targets within two years toward Net-Zero GHG emissions across the value chain.
How the JT Group plans to achieve Net-Zero
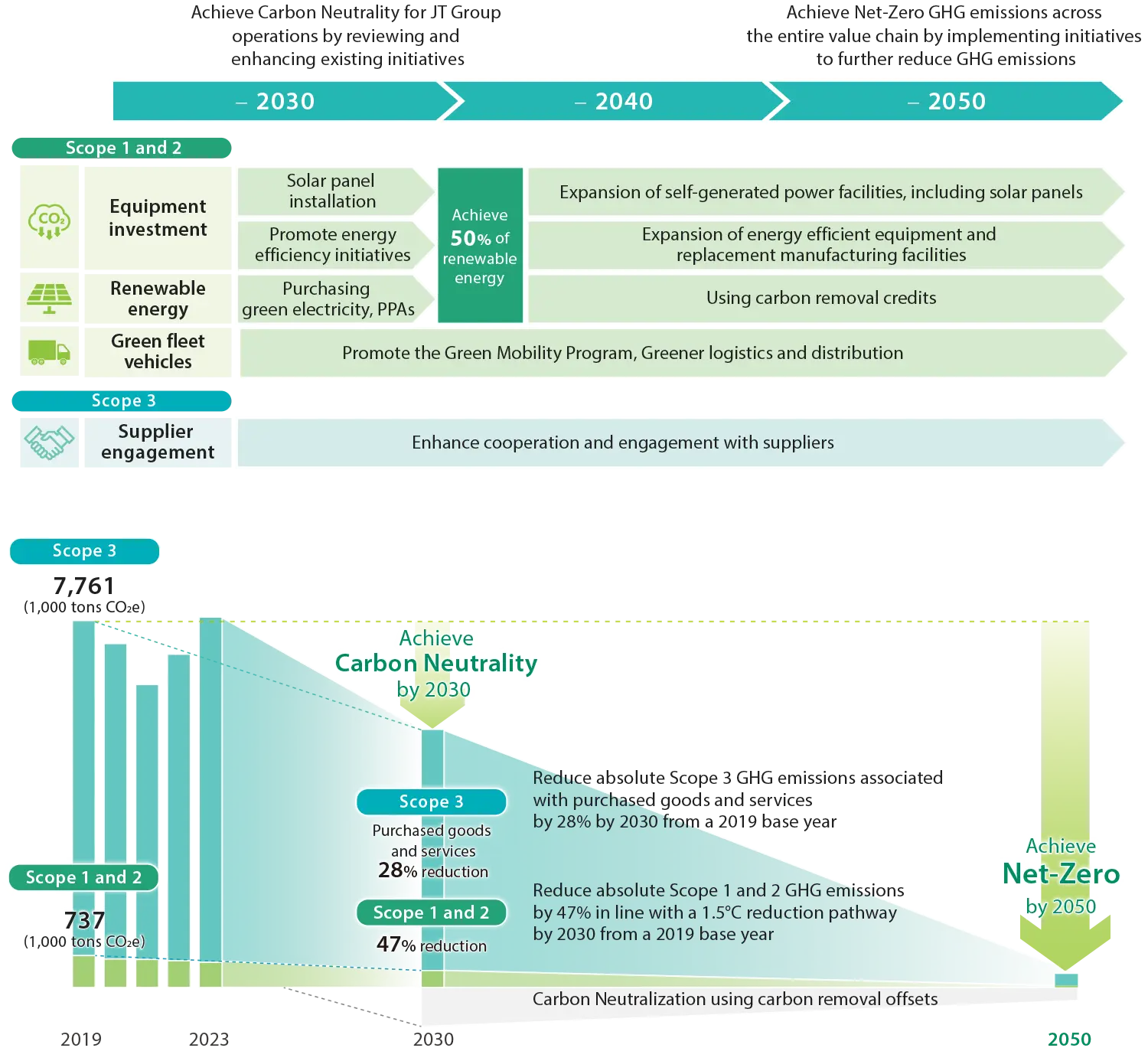
Note:
These are the plans as of May 31 2024, and they are subject to revision in accordance with future business strategies
Climate change
Climate change is one of the most serious environmental challenges our society and businesses have ever faced. Manifesting as the greenhouse effect, extreme weather and the like, climate change affects not just the supply chain for our products, made mainly through agricultural production, but our operations worldwide as well. Addressing this challenge is therefore a serious commitment for the Group. Working to reduce GHG emissions over the long term, we are contributing to global measures against climate change. In February 2022, we announced our ideal of entirely carbon-neutral operations by 2030. This is an ambitious, science-based objective. In 2022, SBTi validated targets set by the Group in pursuit of limiting the increase in global average temperature to less than 1.5°C above pre-industrial levels. In June 2024, we submitted a commitment letter declaring to make science-based GHG emissions reduction targets within two years toward Net-Zero GHG emissions across the value chain by 2050.
The JT Group has been disclosing information in accordance with the Task Force on Climate-related Financial Disclosures framework.
Indicator |
Description |
|---|---|
Governance |
Climate-related issues are of strategic importance to our business. Through our business-wide enterprise risk management process, we have identified climate-related risk as one of the enterprise-level risks for our tobacco business, which also needs to be considered in local risk inventories and assessment processes. Board oversight is critical and climate-related issues, especially those that may have impacts on business strategy, are brought up in quarterly Board-level meetings. See Corporate governance for the ESG-related index for executive remuneration. Our corporate governance position and structure can be found on the JT website |
Strategy |
Through climate scenario analysis performed in 2019, we identified two main risks: potential cost increases due to governments raising carbon taxes to further reduce GHG emissions and the impact on tobacco leaf growing due to changes in environmental conditions. Our plan is to mitigate these risks by continuing to implement climate-related initiatives across our value chain and address areas for improvement. See the JT website for general information on environmental initiatives and Risk factors. |
Risk management |
We consider climate-related risks and identify risk mitigation and management approaches through our enterprise risk management (ERM) process. We also include these risks in local risk inventories, assessment processes, and action plans, which are partly based on our ongoing country-level climate scenario analyses. We will compare business-wide risks from local assessments and identify the most critical ones. |
Metrics and targets |
Our JT Group Environment Plan 2030 includes a commitment to reduce GHG emissions from our own operations by 47% (2030 versus 2019). We have also set a longer-term GHG emissions reduction target, as well as targets for renewable electricity, backed by our Group-wide climate scenario analysis. Read more about the JT Group Environment Plan 2030, Environmental data/External verification and Data calculation/consolidation methods on JT.com. |
Scenario analysis
To identify risks and opportunities for our business related to climate change, the Group conducted scenario analyses using multiple scenarios (1.5°C, 4°C, etc.). In conducting these analyses, we utilized scenarios based on typical concentration pathways outlined by the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC), such as Representative Concentration Pathways (RCP2.6, RCP8.5). As a result of the analyses, we identified two major climate-related risks: carbon pricing (increased carbon taxes) and changes in growing environments due to rising average temperatures.
Risks and opportunities |
Applied scenarios and financial impacts (billion yen) |
Time frame |
Impacts |
Countermeasures |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
1.5℃ |
4℃ |
Short |
Medium |
Long |
||||
Transition risks |
Measures and policies to address climate change effect |
-8.5 |
-2.8 |
● |
● |
● |
|
|
Carbon pricing |
-108.9 |
-2.7 |
● |
● |
● |
|
|
|
Demand/supply shift for materials and energy |
-0.9 |
3.3 |
● |
● |
● |
|
|
|
Physical risks |
Changes in farming environments due to rising average temperatures |
-3.5 |
-34.8 |
● |
● |
● |
|
|
More frequent, larger-scale abnormal climatic events |
-7.1 |
-18.8 |
● |
● |
● |
|
|
|
Tight water supply |
-0.1 |
-0.1 |
|
● |
● |
|
|
|
Opportunities |
Changes in customer lifestyles |
0.1 |
0.7 |
|
● |
● |
|
|
Effects of rising temperatures on supplier locations and methods |
0.2 |
1.1 |
|
● |
● |
|
|
|
- Read more about climate scenario analysis on JT.com.
Biodiversity
Believing that the sustainability of people’s lives and corporate operations is possible only when nature and society are sustainable, the JT Group has made biodiversity preservation a high priority. By understanding how our businesses affect and depend on ecosystems, we are working harder to preserve biodiversity.
Risk assessment
In 2022, we undertook a qualitative assessment of the effects of our tobacco business and its dependence on ecosystems, based on TNFD v0.3 and the International Union for Conservation of Nature’s guidelines. We assessed our impact on natural resources at each stage of business, namely material procurement, production and disposal, as well as the scope and gravity of the influence, to identify where our impact on ecosystems is greatest. We did the same assessment and identification concerning dependencies.
Business effects and dependence on biodiversity
In tobacco leaf production, land use and soil pollution in Brazil were identified as the strongest effects of our business on biodiversity, and that holds true in other tobacco producing nations. On the dependency side, we found that our tobacco business greatly depends on a range of ecosystem services, such as protection from flooding and storm damage and land stabilization and erosion prevention in Brazil, and we found similar tendencies in other tobacco-producing nations.
Early-stage analysis of risks and opportunities
We identified the effects of landslides and floods, consequences of progressive soil deterioration following forest development, and overuse of agricultural chemicals as major risks to production volume and quality of tobacco leaf. We believe we can reduce such risks to some degree and discover more opportunities to procure tobacco leaf in reliable, sustainable ways by following through on our initiatives to maintain and enhance ecosystem services like tree-planting and agrichemical restrictions.
Reducing impact and dependence on biodiversity
We are working to reduce both the impact and dependence on biodiversity of our Tobacco business, with reference to the AR3T framework, based on the Science-Based Targets for Nature guidance, from the standpoints of avoidance, reduction, regeneration, restoration and transformation. We avoid the use of toxic agrichemicals and replace them with safer, more environment-conscious products. We reduce waste by managing the safety and possible impacts of our products and packaging on society and the environment throughout their life cycles, and by operating systems designed for effective recycling of products as resources and managing industrial waste. The Group helps preserve forests by assisting with natural regeneration. In Zambia, we participate in the Shishamba Forest Livelihoods Project for sustainable management of the Miombo woodlands. In Brazil, we work to restore over 300 hectares of permanently protected areas in partnership with research institutes, environmental-education organizations and the nation’s National Bank for Economic and Social Development. As part of this transformation, we have been accelerating our efforts to organize and standardize data pertinent to biodiversity preservation in partnership with the international non-profit LIFE Institute since 2017.
Protecting water
Water is an important natural resource for our business activities, and we have already achieved a 15% reduction in water withdrawal associated with our tobacco business compared to 2015 levels, a target of the JT Group Environment Plan 2030, ahead of schedule. Under the JT Group Sustainability Targets, we have set our own independent standards that reflect or exceed those of laws and regulations, including more ambitious targets for water withdrawal reduction and targets related to preventing water pollution so as to minimize impacts on ecosystems, and we monitor our performance. We require all of our tobacco leaf suppliers to produce high-quality tobacco leaf and implement our GAP Protocol with a view to protecting ecosystems. This not only increases the economic sustainability of the tobacco leaf growers, but also prevents the risk of water pollution with nitrate nitrogen, a highly water soluble compound that is incorporated in many chemical fertilizers and agrichemicals that are widely used on agricultural land.
Enhancing biodiversity - No deforestation, no conversion
We have a target to totally replace the naturally obtained wood that our directly contracted tobacco leaf suppliers use to dry tobacco leaves with renewable fuel resources by 2030. We use the Agroforestry app to log annual tree-planting progress in tobacco farmlands in Tanzania, Zambia and Brazil. The JT Group also works to achieve Net-Zero destruction of the forests it manages across its entire supply chain for the tobacco business by 2030.
Waste reduction
We have already achieved our JT Group Environment Plan 2030 target of a 20% reduction in the volume of waste associated with our tobacco business compared to 2015 levels ahead of schedule, and we have now set a more ambitious target in the JT Group Sustainability Targets. In addition to reducing waste generated in our business activities and changing our waste disposal methods, we have also incorporated initiatives related to products used by consumers with the goal of reducing environmental impacts throughout the value chain. Targeting zero factory waste to landfills by 2030, we are reducing the use of packaging materials that contain plastic, and aiming to have 100% of our packaging made from recycled or recyclable materials by 2030.
Collaboration with suppliers
Collaboration with suppliers is important for understanding and improving our impacts on ecosystems, including realizing Net-Zero GHG emissions throughout the value chain.
To reduce Scope 3 GHG emissions, we are using a supply chain program provided by CDP, an international environmental NGO, to help us ascertain environmental information related to diverse suppliers associated with our business, including suppliers of raw materials, such as tobacco leaf, and logistics companies.
By doing so, we have strengthened our engagement with suppliers, enabling us to identify environmental risks and business opportunities in the value chain, and we are now examining and implementing measures for more efficient energy use and reduction of GHG emissions.
We will be constantly mindful of what the JT Group can achieve as we continue to collaborate with suppliers in committed efforts to preserve healthy relationships between nature, people, and companies.

